
Andropause: How Low Testosterone Impacts Bone Health in Aging Men
- TFacts Staff

Andropause is the natural and age-linked decline of growth and testosterone hormone levels in men. It also goes by many terms, such as male menopause, androgen partial androgen deficiency in aging males (PADAM), androgen deficiency in aging males (ADAM), and viropause. Andropause usually involves a reduction in testosterone production in males aged 50 and above and is affiliated with hypogonadism, a condition that involves reduced testosterone levels and related symptoms.
Testosterone is crucial in the overall well-being and health of men. It is responsible for many functions in the body, and one of its important roles is bone health. Knowing the relationship between low testosterone and bone health is crucial to addressing and preventing potential health risks.
In this blog, we will explore andropause in men and how low testosterone impacts bone health in aging men so individuals can properly understand the role of testosterone in bone health, allowing them to properly understand the question ‘How low testosterone impacts bone health in aging men.’
Table of Contents
ToggleWhat is Andropause?
Andropause is a term that refers to the condition where men experience a decline in testosterone levels. It usually occurs during middle age. Andropause can cause psychological, sexual, and physical problems and can worsen while growing older.
Some of the symptoms include sadness or depression, low energy, difficulty concentrating, reduced confidence, reduced motivation, infertility, reduced libido, erectile dysfunction, decreased bone density, feelings of physical weakness, reduced muscle mass, increased muscle mass difficulty sleeping or insomnia, infertility, and reduced libido.
Low testosterone levels have been associated with androgen and also osteoporosis. A situation where an individual’s bones are brittle and weak.
The Role of Testosterone Levels in Bone Health
Many studies have shown a strong relationship between testosterone and bone health. Testosterone has an important role in maintaining bone strength and density. It helps produce osteoblasts, cells that help build bone tissue.
These cells usually work continuously to produce new bone and ensure your skeletal system is healthy and strong. Testosterone also helps reduce bone resorption, which is the process of breaking old bone tissue. The balance between bone formation and breakdown is essential for maintaining excellent bone density.
However, low testosterone levels can affect this balance. Low testosterone levels affect the production of osteoblasts and cause a reduction in bone formation.
Simultaneously, bone resorption might surpass bone formation which will result in the net loss of bone tissue. Therefore, people with low testosterone levels might experience reduced bone density and enhanced fracture risk.
Testosterone and its role in bone growth and repair
Aside from testosterone’s impact on bone density, it also plays an essential role in the growth and repair of bones. During puberty, testosterone adds to the maturation and growth of bones. It stimulates growth plate closure and signals the end of vertical bone growth.
The process makes sure individuals can reach their maximum height. Moreover, testosterone can also help in bone repair and healing of damages or microfractures that might occur due to trauma or physical activity.
The role of testosterone in bone repair and growth doesn’t end in puberty. Throughout the life of an individual, the appropriate testosterone levels are critical for maintaining excellent health.
However, while aging, bone density decreases naturally. This makes us prone to fractures and osteoporosis. However, according to studies, maintaining optimal testosterone levels helps reduce age-related bone loss and risk of fractures.
The Relationship Between Testosterone and Osteoporosis
Osteoporosis is a condition that is marked by brittle and weakened bones. This makes the bones prone to fractures.
Though osteoporosis is usually associated with women, men also develop it, and low testosterone has an impact on this condition. In bone health, testosterone isn’t just for strength and muscle mass. It also helps maintain our bone density.
Osteoporosis commonly occurs due to an imbalance between bone resorption and bone formation. This results in increased bone fragility and bone loss. In bone remodeling, old bones are broken down by the cells known as osteoclasts, while new bones are formed by the cells known as osteoblasts.
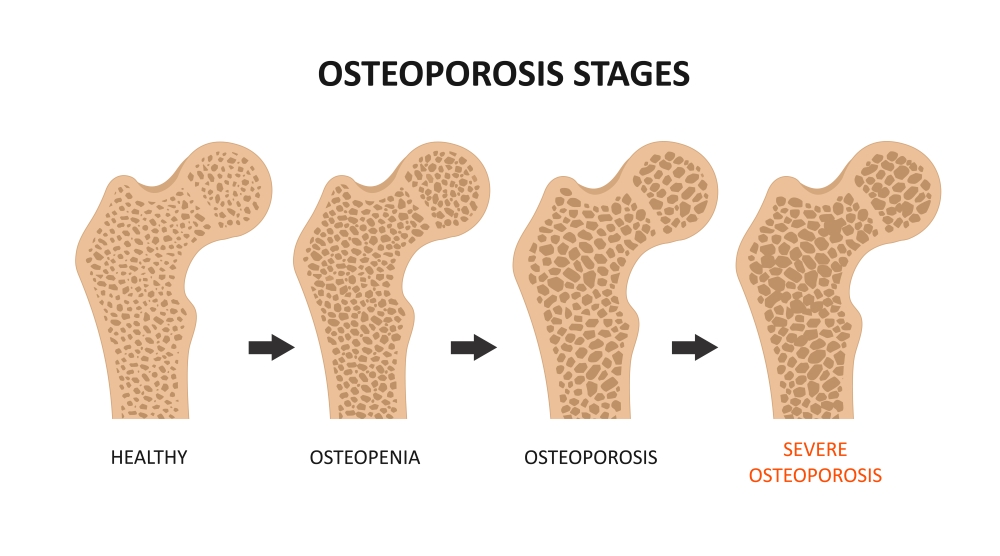
The continuous process of the above methods helps maintain bone structure and strength. But, when there is an imbalance, it results in osteoporosis. This disruption can be due to various factors, such as lifestyle choices, nutritional deficiencies, and hormonal changes.
Low testosterone commonly adds to osteoporosis development in men. Since testosterone plays an important role in maintaining our bone density via the stimulation of bone formation and inhibiting bone resorption, low testosterone levels can affect the balance between bone resorption and formation, resulting in decreased bone density.
As a man ages, his testosterone will naturally decline, and the decline can be accelerated by osteoporosis development. The reduction in bone density due to low testosterone labels also increases fracture risk, especially in elderly men. Fractures can even occur with small traumas like minor impacts or simple falls. Therefore, it is crucial to monitor testosterone labels and ensure you address deficiencies to prevent osteoporosis progression.
TRT for Restoring Bone Density
Testosterone replacement therapy is usually recommended for men with low testosterone to help them restore bone density and reduce fracture risk. But, it is essential to consult with health professionals before you begin any hormone therapy.
Apart from testosterone replacement therapy, you can opt for lifestyle modifications to manage osteoporosis. Regular exercises such as weight lifting and walking can help enhance bone strength and density. Balanced diets rich in vitamin D and calcium are also crucial for maintaining healthy bones.
Conclusion
Testosterone is a hormone in the body that manages men’s reproductive health and sex drive. Men produce and require more testosterone than women. Moreover, testosterone naturally declines in men, but unnatural reduction can negatively affect your sex life, mood, and energy and result in andropause.
Additionally, low testosterone impacts bone health in aging men and can result in osteoporosis. If you wish to learn more about andropause and how low testosterone impacts bone health in aging men, visit this website to get answers to your questions.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What is the effect of andropause in men?
The effects in men usually include depression, erectile dysfunction, loss of sex drive, and other emotional and physical symptoms during their late 40s and early 50s. There are other symptoms such as irritability, mood swings, reduced ability to exercise, and loss of muscle mass.
2. Does low testosterone affect men’s bones?
A major clinical symptom of low testosterone in men is a sharp reduction in bone density. In some case-controlled studies, experts noted that in hypogonadal men, bone mineral density is commonly linked to a huge increase in bone fractures.
3. Does low testosterone affect older men?
According to this study, about 30% of men who are 60 years old and older are evaluated to have low testosterone. Low testosterone commonly goes along with symptoms and signs such as low muscle and bone mass, enhanced fat mass (more commonly central adiposity), impaired cognitive, sexual, and physical function, and low energy.




