
Does Beer Help Testosterone?
- TFacts Staff

The relationship between beer consumption and testosterone levels is not straightforward and remains unclear. Although some studies suggest that moderate alcohol consumption may have a slight positive impact on testosterone levels, especially in older men, other studies indicate that chronic or excessive alcohol consumption can have adverse effects on testosterone levels.
Table of Contents
ToggleBeer Composition and Ingredients:
Hops are plants that contribute to the bitterness and scent of beer. They include chemicals known as phytoestrogens, which are weak copies of the human hormone estrogen. When you consume beer containing hops, phytoestrogens can interfere with your hormone levels.
Beer is made from barley, a type of grain. It gives the carbohydrates that yeast uses to generate alcohol during fermentation. While barley does not directly alter hormone levels, it is an important ingredient in beer making.
Yeast is a fungus that ferments sugars in beer, producing alcohol and carbon dioxide. While yeast is necessary for beer production, it has little effect on hormone levels when consumed.
Impact of alcohol on hormone levels
Alcohol Metabolism:
When you consume alcohol, your body mostly metabolizes it in the liver. This process consists of numerous phases, including converting alcohol into acetaldehyde and ultimately into acetate, which your body can use as energy.
Hormonal Regulation:
Hormones are chemical messengers in the body that control various physiological processes, including metabolism, growth, and reproduction. Testosterone is a hormone largely connected with male reproductive activity, but it is found in both men and women in varying amounts.
Effects on Testosterone:
The National Institute of Health, published a journal on acute alcohol consumption, or drinking alcohol in a single session, can temporarily raise testosterone levels. This rise could be attributed to alcohol’s impact on lowering the production of SHBG (sex hormone-binding globulin), a hormone that binds to testosterone and limits its availability.
However, long-term or severe alcohol usage can have the opposite impact. Long-term alcohol usage can interfere with the normal function of the hypothalamic-pituitary-gonadal (HPG) axis, which controls testosterone production. This disturbance can result in lower testosterone levels over time.
Alcohol can impact the production of testosterone by affecting the Leydig cells in the testes, which may lead to decreased levels of testosterone.
Impact of Alcohol Type and Quantity:
Alcohol’s effects on testosterone levels vary depending on the type of alcohol ingested (e.g., beer, wine, spirits), the amount consumed, and the frequency of intake.
While some research indicates that moderate alcohol consumption, including beer, has little influence on testosterone levels, excessive or chronic alcohol consumption is more likely to result in hormonal imbalances.
Individual Variability:
It is critical to note that the effect of alcohol on hormone levels varies by individual. Age, gender, genetics, overall health, and lifestyle behaviors (for example, diet and exercise) can all have an impact on how alcohol impacts hormone control.
Overall Health Implications:
Imbalanced testosterone levels, whether caused by alcohol or other circumstances, can have serious health consequences. Diminished muscle mass, bone density, mood swings, and sexual dysfunction are some of the health concerns linked to low testosterone levels.
Effect of Beer on Testosterone
Controlled experiments or observational studies are commonly used in science. For example, investigations to find out the association between beer consumption and testosterone levels entail giving subjects exact amounts of beer or its components and tracking changes in testosterone levels over time. Observational studies use population data to uncover links between beer consumption trends and testosterone levels.
Moderate Consumption Studies:
Some studies have found that moderate alcohol use, including beer, may have a minor favorable influence on testosterone levels, especially in older men.
For example, a 2003 study published in the journal Alcoholism: Clinical & Experimental Research discovered that moderate alcohol use boosted testosterone levels in healthy males, with the impact being stronger in older people
Effect of Hops and Phytoestrogens:
Hops, an important ingredient in beer, contain phytoestrogens, which are plant-derived chemicals that mimic the function of estrogen in the body. Research suggests that these phytoestrogens may have estrogenic effects in humans and could impact hormone levels, including testosterone. However, the extent to which phytoestrogens from hops in beer alter testosterone levels is still debated and warrants further exploration.
Chronic and Excessive Consumption Studies:
However, studies have found that persistent or severe alcohol intake has a deleterious impact on testosterone levels. Long-term alcohol usage has been linked to hormonal changes, including decreased testosterone synthesis and altered Leydig cell function in the testes. Chronic alcohol intake can also cause liver damage, which adds to hormone imbalances and other health issues.
Individual Variability and Other Factors:
The effect of beer drinking on testosterone levels varies by individual, depending on age, gender, genetics, overall health, and lifestyle choices.
Other components in beer, such as carbohydrates and calories, can indirectly alter hormone levels by affecting metabolism and body composition.
Limitations and Considerations:
Due to constraints such as small sample sizes, confounding variables, and discrepancies in study techniques, the conclusions of studies on beer and testosterone should be interpreted with caution. While some studies suggest that moderate beer drinking may improve testosterone levels, general health factors, particularly the hazards associated with alcohol dependence, should be taken into account.
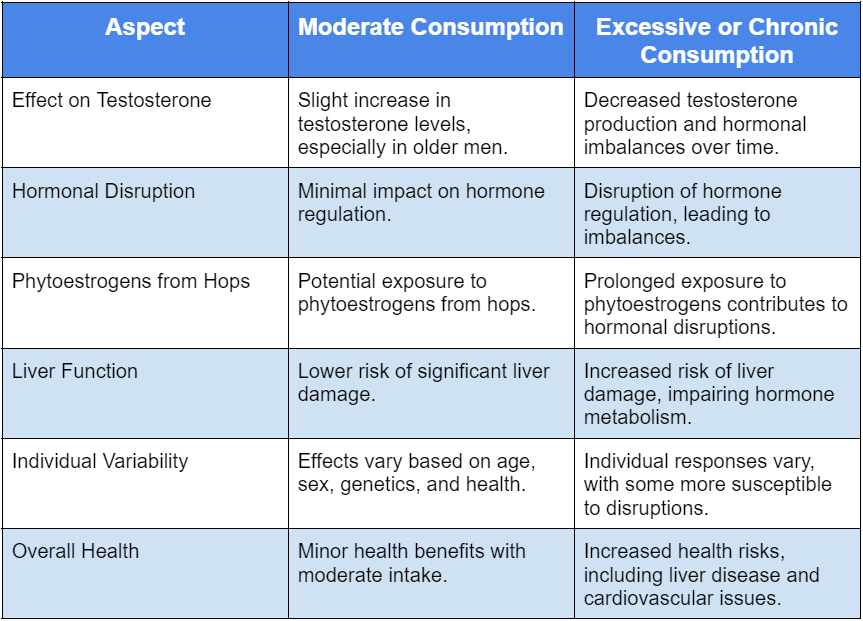
This condensed table compares the effects of moderate beer drinking to high or chronic consumption on testosterone levels and general health:
Alternative Beverages and Testosterone
Beer: As previously mentioned, moderate beer drinking may have a minor favorable influence on testosterone levels, particularly in older men. However, phytoestrogens included in hops in beer may impact hormone levels, and excessive consumption can lead to hormonal abnormalities over time.
Wine: According to some research, moderate wine intake may have slightly favorable impacts on testosterone levels, just as beer. Red wine, for example, contains resveratrol, a molecule with potential health advantages, though the effects on testosterone are not fully understood.
Spirits (e.g., whiskey, vodka): Little study has been done on the impact of spirits on testosterone levels. However, as with other types of alcohol, excessive intake of spirits might affect hormone regulation and metabolism, potentially leading to decreased testosterone production over time.
Non Alcoholic: Water does not directly alter testosterone levels. However, staying hydrated is vital for overall health and can indirectly help with hormone balance.
Milk: It contains a variety of minerals, including protein and calcium, which are beneficial to general health. Little data exists on the direct benefits of milk on testosterone levels, but its nutritious value can help with overall well-being.
Green tea, for example, has antioxidant-rich substances such as catechins and flavonoids. While there is insufficient evidence on tea’s precise effects on testosterone levels, moderate tea consumption can contribute to a healthy lifestyle.
Health Risks with Excessive alcohol consumption
Cardiovascular Health: According to some research, moderate alcohol use, including beer, may reduce the risk of cardiovascular disease. However, heavy drinking might increase the risk of cardiac problems.
Liver Function: While moderate beer drinking may not have a major impact on liver function in healthy people, excessive or chronic consumption can cause liver damage, including alcoholic liver disease.
Mental Health: For some people, moderate alcohol consumption can temporarily improve their mood. However, binge drinking can lead to mental health problems like despair and anxiety.
To Conclude:
Excess alcohol use, regardless of the source (beer, wine, or spirits), is more likely to lower testosterone levels than non-alcoholic beverages such as water, milk, or tea. While beer and wine may have slight benefits for testosterone levels when consumed in moderation, excessive use of any alcoholic beverage can alter hormone regulation and metabolism, resulting in hormonal imbalances and associated health problems.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. Does masturbating reduce testosterone?
Some studies have shown temporary spikes in testosterone after ejaculation, while others have found no significant long-term effects. Overall, regular and moderate masturbation is unlikely to have a significant impact on testosterone levels.
2. Is beer good for testosterone?
While moderate beer consumption may have minor positive effects on testosterone levels, excessive or chronic consumption can lead to hormonal imbalances. Drinking beer in moderation and considering its impact on overall health is essential.
3. Does alcohol affect erection?
Yes, alcohol can impair erectile function. While small amounts of alcohol may initially boost sexual desire and lessen inhibitions, excessive consumption can damage erectile function, making it harder to achieve or maintain an erection. This phenomenon is commonly known as “brewer’s droop” or “whiskey dick.” Alcohol consumption can lead to erectile dysfunction by reducing blood flow to the penis and impairing the nervous system’s ability to convey arousal signals.




